Note
Click here to download the full example code
Monitor custom metrics along hyperoptimization¶
This example shows how to compute customize metrics using a callback function, as in scipy.optimize.
# Authors: Quentin Bertrand <quentin.bertrand@inria.fr>
# Quentin Klopfenstein <quentin.klopfenstein@u-bourgogne.fr>
# Mathurin Massias <mathurin.massias@gmail.com>
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sparse_ho.models import Lasso
from sparse_ho.criterion import HeldOutMSE
from sparse_ho import ImplicitForward
from sparse_ho.utils import Monitor
from sparse_ho.ho import grad_search
from sparse_ho.optimizers import LineSearch
from libsvmdata.datasets import fetch_libsvm
print(__doc__)
# dataset = 'rcv1'
dataset = 'simu'
if dataset == 'rcv1':
X, y = fetch_libsvm('rcv1.binary')
else:
X, y = make_regression(
n_samples=1000, n_features=1000, noise=40, random_state=0)
# The dataset is split in 2: the data for training and validation: X/y and
# the unseen data X_test/y_test, use to assess the quality of the model
X, X_test, y, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.333, random_state=0)
n_samples = X.shape[0]
idx_train = np.arange(0, n_samples // 2)
idx_val = np.arange(n_samples // 2, n_samples)
alpha_max = np.max(np.abs(X[idx_train, :].T @ y[idx_train])) / len(idx_train)
alpha0 = alpha_max / 10
estimator = linear_model.Lasso(
fit_intercept=False, max_iter=1e5, warm_start=True)
Call back definition
Grad-search with sparse-ho and callback¶
Out:
(1.2432848511536219, 1846.3498842875065, -69.01087353749456)
Plot results¶
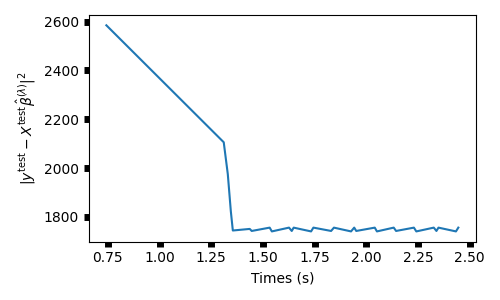
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 3))
plt.plot(monitor.times, objs_test)
plt.tick_params(width=5)
plt.xlabel("Times (s)")
plt.ylabel(r"$\|y^{\rm{test}} - X^{\rm{test}} \hat \beta^{(\lambda)} \|^2$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show(block=False)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.844 seconds)