Note
Click here to download the full example code
Weighted Lasso versus Lasso on MEG¶
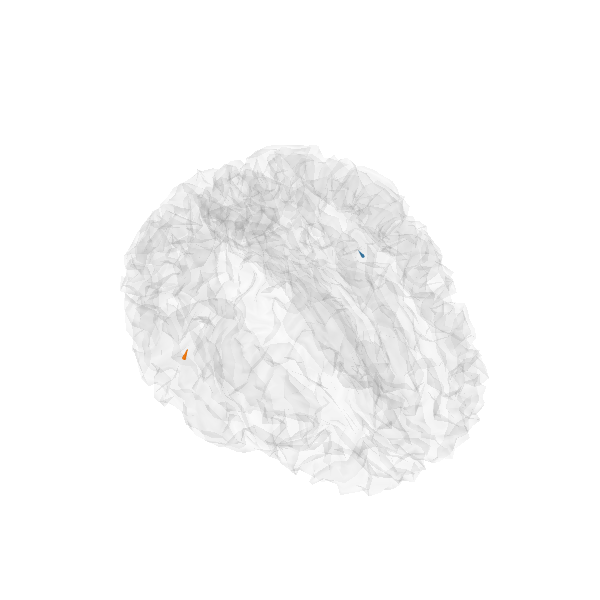
This example compares the Lasso and the weighted Lasso on real MEG data. While the bias of the Lasso leads to optimal coefficients with a lot of sources in the brain, the weighted Lasso is able to recover 1 source per hemisphere in the brain, as expected from a neuroscience point of view.
# Authors: Mathurin Massias <mathurin.massas@gmail.com>
# Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 4
import numpy as np
import mne
from mne.viz import plot_sparse_source_estimates
from mne.datasets import sample
from mne.inverse_sparse.mxne_inverse import (
_prepare_gain, is_fixed_orient, _reapply_source_weighting,
_make_sparse_stc)
from celer import Lasso as celer_Lasso
from sparse_ho.utils import Monitor
from sparse_ho.models import WeightedLasso, Lasso
from sparse_ho.criterion import FiniteDiffMonteCarloSure
from sparse_ho import Implicit
from sparse_ho.ho import grad_search
from sparse_ho.optimizers import GradientDescent
def apply_solver(
evoked, forward, noise_cov, loose=0.2, depth=0.8, p_alpha0=0.7,
model_name="wlasso"):
"""Call a custom solver on evoked data.
This function does all the necessary computation:
- to select the channels in the forward given the available ones in
the data
- to take into account the noise covariance and do the spatial whitening
- to apply loose orientation constraint as MNE solvers
- to apply a weighting of the columns of the forward operator as in the
weighted Minimum Norm formulation in order to limit the problem
of depth bias.
Parameters
----------
evoked : instance of mne.Evoked
The evoked data
forward : instance of Forward
The forward solution.
noise_cov : instance of Covariance
The noise covariance.
loose : float in [0, 1] | 'auto'
Value that weights the source variances of the dipole components
that are parallel (tangential) to the cortical surface. If loose
is 0 then the solution is computed with fixed orientation.
If loose is 1, it corresponds to free orientations.
The default value ('auto') is set to 0.2 for surface-oriented source
space and set to 1.0 for volumic or discrete source space.
depth : None | float in [0, 1]
Depth weighting coefficients. If None, no depth weighting is performed.
p_alpha0 : float (default=0.7)
Proportion of alpha_max for the initial point alpha0.
model_name : string (default="wlasso")
Name of the model to use, "lasso" or "wLasso" in this case.
Returns
-------
stc : instance of SourceEstimate
The source estimates.
"""
all_ch_names = evoked.ch_names
# Handle depth weighting and whitening (here is no weights)
forward, gain, gain_info, whitener, source_weighting, _ = _prepare_gain(
forward, evoked.info, noise_cov, pca=False, depth=depth,
loose=0, weights=None, weights_min=None, rank=None)
# Select channels of interest
sel = [all_ch_names.index(name) for name in gain_info['ch_names']]
M = evoked.data[sel]
# Whiten data
M = np.dot(whitener, M)
n_orient = 1 if is_fixed_orient(forward) else 3
X, active_set, monitor = solver(
M, gain, n_orient, evoked.nave, p_alpha0=p_alpha0,
model_name=model_name)
X = _reapply_source_weighting(X, source_weighting, active_set)
stc = _make_sparse_stc(X, active_set, forward, tmin=evoked.times[0],
tstep=1. / evoked.info['sfreq'])
return stc, monitor
Define your solver
def solver(
y_train, X_train, n_orient, nave, p_alpha0=0.7, model_name="wlasso"):
n_times = y_train.shape[1]
idx_max = np.argmax(np.sum(y_train ** 2, axis=0))
y_train = y_train[:, idx_max]
n_samples, n_features = X_train.shape
alpha_max_old = (np.abs(X_train.T @ y_train)).max() / n_samples
X_train /= alpha_max_old
alpha_max = (np.abs(X_train.T @ y_train)).max() / n_samples
alpha0 = p_alpha0 * alpha_max
estimator = celer_Lasso(
fit_intercept=False, max_iter=100, warm_start=True,
tol=1e-3)
if model_name == "wlasso":
alpha0 = alpha0 * np.ones(n_features)
model = WeightedLasso(estimator=estimator)
else:
model = Lasso(estimator=estimator)
sigma = 1 / np.sqrt(nave)
criterion = FiniteDiffMonteCarloSure(sigma=sigma)
algo = Implicit()
optimizer = GradientDescent(
n_outer=4, tol=1e-7, verbose=True, p_grad_norm=1.9)
monitor = Monitor()
grad_search(algo, criterion, model, optimizer,
X_train, y_train, alpha0, monitor)
X = criterion.dense0[:, np.newaxis] * np.ones((1, n_times))
active_set = criterion.mask0
X /= alpha_max_old
return X, active_set, monitor
data_path = sample.data_path()
fwd_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-eeg-oct-6-fwd.fif'
ave_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-ave.fif'
cov_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-shrunk-cov.fif'
condition = 'Left Auditory'
Out:
Using default location ~/mne_data for sample...
Attempting to create new mne-python configuration file:
/home/circleci/.mne/mne-python.json
Read noise covariance matrix and evoked data
noise_cov = mne.read_cov(cov_fname)
evoked = mne.read_evokeds(ave_fname, condition=condition, baseline=(None, 0))
evoked.crop(tmin=0.04, tmax=0.18)
# Crop data around the period of interest
evoked = evoked.pick_types(eeg=False, meg=True)
Out:
365 x 365 full covariance (kind = 1) found.
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 59) active
Reading /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-ave.fif ...
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
Found the data of interest:
t = -199.80 ... 499.49 ms (Left Auditory)
0 CTF compensation matrices available
nave = 55 - aspect type = 100
Projections have already been applied. Setting proj attribute to True.
Applying baseline correction (mode: mean)
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
Handling forward solution
forward = mne.read_forward_solution(fwd_fname)
loose, depth = 0., .8 # corresponds to free orientation
Out:
Reading forward solution from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-eeg-oct-6-fwd.fif...
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
2 source spaces read
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read MEG forward solution (7498 sources, 306 channels, free orientations)
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read EEG forward solution (7498 sources, 60 channels, free orientations)
MEG and EEG forward solutions combined
Source spaces transformed to the forward solution coordinate frame
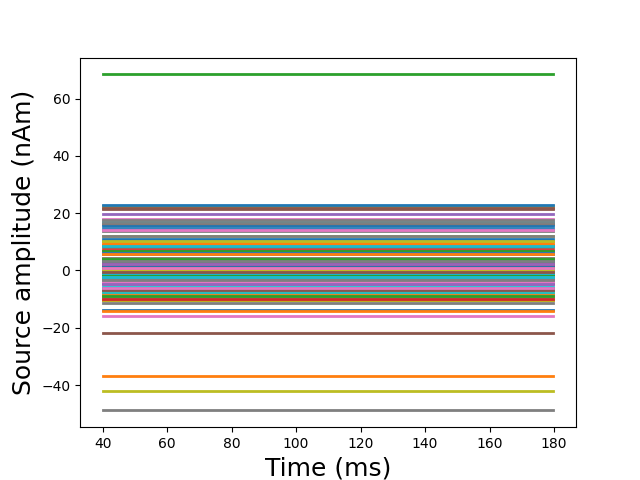
Run estimation with Lasso
stc = apply_solver(
evoked, forward, noise_cov, loose, depth, model_name="lasso")[0]
# Plot glass brain
plot_sparse_source_estimates(
forward['src'], stc, bgcolor=(1, 1, 1), opacity=0.1)

Out:
Converting forward solution to fixed orientation
Average patch normals will be employed in the rotation to the local surface coordinates....
Converting to surface-based source orientations...
[done]
info["bads"] and noise_cov["bads"] do not match, excluding bad channels from both
Computing inverse operator with 305 channels.
305 out of 366 channels remain after picking
Selected 305 channels
Creating the depth weighting matrix...
Whitening the forward solution.
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 3)
Computing rank from covariance with rank=None
Using tolerance 3.5e-13 (2.2e-16 eps * 305 dim * 5.2 max singular value)
Estimated rank (mag + grad): 302
MEG: rank 302 computed from 305 data channels with 3 projectors
Setting small MEG eigenvalues to zero (without PCA)
Creating the source covariance matrix
Adjusting source covariance matrix.
Iteration 1/4 ||Value outer criterion: 3.75e+01 ||norm grad 2.05e+01
Iteration 2/4 ||Value outer criterion: 9.09e+00 ||norm grad 4.12e+00
Iteration 3/4 ||Value outer criterion: 7.16e+00 ||norm grad 2.73e-01
Iteration 4/4 ||Value outer criterion: 5.64e+00 ||norm grad 2.90e-02
Total number of active sources: 150
((vtkmodules.vtkRenderingOpenGL2.vtkOpenGLActor)0x7f1a619aa280, PolyData (0x7f1a619aa3a0)
N Cells: 16384
N Points: 312273
X Bounds: -1.164e+01, 1.050e+01
Y Bounds: -1.070e+01, 1.754e+01
Z Bounds: 2.075e+00, 2.232e+01
N Arrays: 1
)
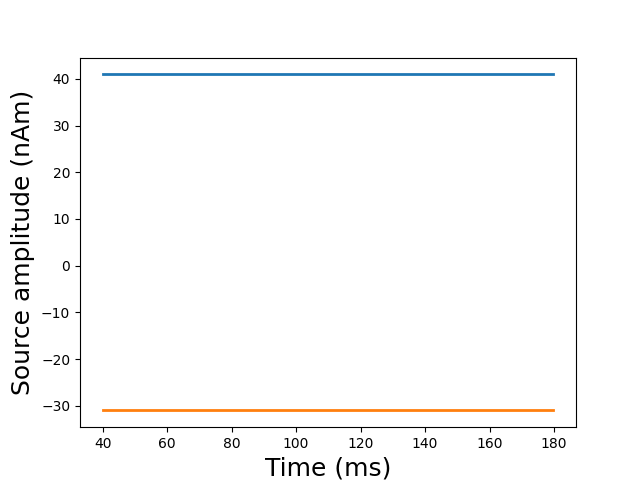
Run estimation with Weighted Lasso
stc = apply_solver(
evoked, forward, noise_cov, loose, depth, model_name="wlasso")[0]
# Plot glass brain
plot_sparse_source_estimates(
forward['src'], stc, bgcolor=(1, 1, 1), opacity=0.1)

Out:
Converting forward solution to fixed orientation
Average patch normals will be employed in the rotation to the local surface coordinates....
Converting to surface-based source orientations...
[done]
info["bads"] and noise_cov["bads"] do not match, excluding bad channels from both
Computing inverse operator with 305 channels.
305 out of 366 channels remain after picking
Selected 305 channels
Creating the depth weighting matrix...
Whitening the forward solution.
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 3)
Computing rank from covariance with rank=None
Using tolerance 3.5e-13 (2.2e-16 eps * 305 dim * 5.2 max singular value)
Estimated rank (mag + grad): 302
MEG: rank 302 computed from 305 data channels with 3 projectors
Setting small MEG eigenvalues to zero (without PCA)
Creating the source covariance matrix
Adjusting source covariance matrix.
Iteration 1/4 ||Value outer criterion: 3.75e+01 ||norm grad 2.05e+01
Iteration 2/4 ||Value outer criterion: 2.68e+01 ||norm grad 2.20e+01
Iteration 3/4 ||Value outer criterion: 1.59e+01 ||norm grad 7.05e-01
Iteration 4/4 ||Value outer criterion: 1.54e+01 ||norm grad 4.88e-02
Total number of active sources: 2
((vtkmodules.vtkRenderingOpenGL2.vtkOpenGLActor)0x7f1a64002160, PolyData (0x7f1a640093a0)
N Cells: 16384
N Points: 312273
X Bounds: -1.164e+01, 1.050e+01
Y Bounds: -1.070e+01, 1.754e+01
Z Bounds: 2.075e+00, 2.232e+01
N Arrays: 1
)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 8.100 seconds)